(17669 products available)


















































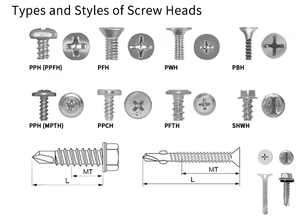
















































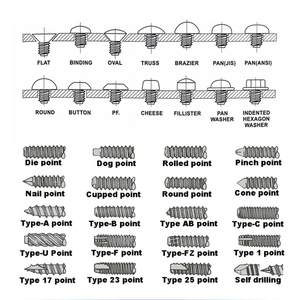














































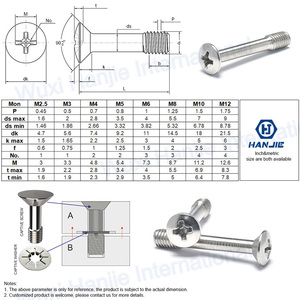




























M2 screws are crafted in different types to meet the specific requirements of diverse tasks.
Straight M2 Screws
Straight M2 screws are the most commonly applied screws when securing objects where a fine, smooth finish is considered mandatory. Their main feature is the straight, vertical lines on the tip and shaft, which offer a good grip and easy application. Straight M2 screws are regularly used in electronics and small machines, where precision is essential. Also, in lighter materials like plastic and thin metal, these screws provide secure fastening without over-embedding, which might damage the delicate workpieces.
Cross Slot M2 Screws
Cross slot M2 screws are engineered with a cross slot on the tip, thus providing better torque control. The design reduces the occurrence of screwdrivers slipping out of the screw head during installation. Cross slot M2 screws are particularly useful in applications where a higher force is needed. Regular usage includes installation in wood, soft metals, and medium-density fiberboard (MDF). Also, these screws are handy in situations where the screw needs to be tightened or loosened frequently, due to the ability to use either a Philips or slotted screwdriver.
Hex Head M2 Screws
Hex head M2 screws have a hexagonal shape on the screw head, requiring a wrench or hex screwdriver for installation. This provides a more substantial torque application, resulting in a tighter fit. Also, hex head M2 screws are widely used in heavy-duty applications like machinery and automotive, where higher strength and durability are primary requirements. They are ideal for use in situations where a high-load or high-stress environment would be detrimental to normal wear and tear in other screw types.
Socket Head Cap Screws
Socket head cap screws also offer high torque capability and are characterized by their cylindrical head with an internal hex (Allen) drive. This makes them favorable for use in tight spaces where a hex key can easily be used to fasten. Made from stronger materials than ordinary screws, these have better fatigue resistance. Typical usage is often seen in the machinery assembly, automotive components, or any device that requires strength and longevity with minimal risk of loosening over time.
Countersunk M2 Screws
Countersunk M2 screws feature a cone-shaped head that allows the screw to sit flush with the surface of the material. This ensures a smooth finish free of protruding elements, ideal for surfaces where aesthetics and safety are concerned. Used in wooden and composite materials, these screws help avoid splintering or damage to the surface. For that reason, they have a wide application in the furniture industry, cabinetry, or installation of drywall, where both strength and appearance come into play.
M2 screws have specific material construction, enhancing durability and making them suitable for various applications.
Stainless Steel M2 Screws
Stainless steel M2 screws are so well applied because they are rustproof and corrosion-resistant. The major elements found in the steel are chromium and nickel, forming a thin layer of oxide that shields the screw from environmental elements such as moisture and chemicals. Its anti-corrosion properties make stainless steel M2 screws suitable for use in areas of great humidity or exposure to chemicals, such as marine applications, outdoor equipment, and even the food processing industry. More so, stainless steel also comes with tensile strength, providing long-lasting performance even under stressful conditions.
Carbon Steel Screws
As an option, M2 screws can also be manufactured from carbon steel, which gives them an advantage in strength and wear resistance. The type of steel can be alloyed with other metals or simply be absorbed by carbon to increase its hardness and edge retention. This makes carbon steel M2 screws ideal for use in heavy-duty applications where strength is critical. Simply, to protect them from rusting, these are normally coated with some zinc or black oxide finish. While less corrosion-resistant than stainless, a coated carbon steel M2 screw provides both strength and moderate protection in industrial or manufacturing and assembly applications.
Brass Screws
Among the available screws, brass M2 screws are manufactured from an alloy of copper and zinc. Often considered for their attractive golden finish, it does not contribute much to their functionality, as it also has excellent corrosion resistance. Brass is a non-magnetic material, making the brass M2 screws ideal for electrical and electronic devices where magnetism should be avoided. Besides, brass is softer by grains and allows easy embedding into softer materials like plastic, wood, and fibers. For this reason, it is commonly used in applications where electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion play a vital role, including marine hardware, musical instruments, and electrical devices.
Coated Steel Screws
Coated steel M2 screws use carbon steel and coat it with other corrosion-resistant materials, such as zinc or anti-corrosive polymers. This coating gives the screw increased durability and resistance to environmental effects, such as moisture and chemicals. These screws are solidly built and resist corrosion, making them excellent fasteners for outdoor or industrial applications. The coating is handy, as it can be clear for aesthetic purposes or contain an anti-corrosive element specific to the application where the screw will be used. This refers to the combination of strength, increased corrosion resistance, and versatility for different environments.
Electronics
Also known as small machine screws, M2 screws are fasteners found in many electronic devices. They are ideal for securing delicate components such as circuit boards, screens, and casings, as they do not damage the material while holding components together tightly. Applied in smartphones, laptops, and medical equipment. They ensure precision and reliability, which are very important in the electronic industry.
3D Printing
M2 screws are also popular in 3D printing since the printing process requires making the printer parts and models with precision. They are used to assemble the printer's frame, nozzle, and other structural components to ensure the printer functions smoothly. Proper fastening ensures accurate prints and machine reliability. M2 screws are important for people who like 3D printing and need good quality prints.
Mechanical Engineering
M2 screws, thanks to their small size and strength, are an important part of mechanical engineering for systems requiring fine components. Applications include precision gears, small motors, and intricate mechanical assemblies in robotics or small machines. Their ability to provide reliable fastening in compact spaces makes them a key input in designs where space is limited and accuracy is vital for optimal performance. Any professional or company in mechanical engineering will appreciate the important role these screws play in creating complex systems that work smoothly.
Model Making
M2 screws are a major component in model making because they allow builders to assemble model kits for machines, vehicles, and architectural structures. Since the screws are small, they are good for fine details and help hold parts together without being seen much. Used by hobbyists and professionals, they are crucial to producing strong and well-finished models that look good and can stand up to handling.
Medical Instruments
The small size and implant-grade materials used in making M2 screws have made them a choice fastening for medical instruments. These offer tight assembly of surgical tools, diagnostic machines, and implants. Very important in the medical field, these screws have great strength, do not corrode, and are light, thus making them ideal for use in life-saving devices and trusted durable components for high-risk applications.
Material
To select M2 screw material, think about the project environment and the required strength. Stainless steel screws are best for outdoor or wet regions, while brass screws look good and resist corrosion. Carbon steel screws offer great strength and are ideal for heavy work. Generally, choose a material that will suit the environment and ensure a long-lasting hold for all components.
Coating and Finish
Corrosion prevention is the primary advantage of coatings and finishes. Zinc-coated M2 screws and polymer-coated screws provide corrosion resistance, making a good choice for exterior environments. Besides, electroplated or well passivated screws help provide additional aesthetic value and corrosion protection. So, choose a screw with the right coating to enhance durability.
Head Type
The head type of the screw chosen will generally depend on the tool usage and the application. Slotted heads are simple but not provide the best grip, as cross slots and socket heads give a better grip and torque for delicate tasks. Hex heads are good for projects that need a strong hold. As such, choose the head type depending on the tools available and the project requirements.
Thread Pitch
The M2 screw thread pitch determines the hold capability on a surface. In particular, finer threads are suitable for thin materials as they allow a deeper embed. In contrast, coarser threads are good for thicker materials as just enough hold is provided. Therefore, while selecting screws to bear in mind that material thickness determines thread pitch and find the right thread pitch for that material.
Screw Length
As for the length of a screw, it must be sufficient for penetration in more than one material layer, allowing it to securely hold two together. An overly long screw may cause material weakening by going too deep into it, while a short one might not give the needed hold. The general rule is to select screws that match the thickness of materials the two need to be joined together.
A1: The M2 screw's diameter is 2 mm, while the standard M2 screw length varies around 4 to 100 mm.
A2: M2 screws are used in fastening electronic and mechanical components, model making, medical instruments, and 3D printing. They are also used in precision engineering because of their small size, strength, and resistance to corrosion.
A3: In order to properly install an M2 screw, it is required to use the correct sized driver to avoid damaging the screw head. The screw is then aligned perpendicularly to the surface of the materials to avoid threading misalignment. While holding the item in place, light pressure is applied in a clockwise direction until the screw is embedded securely but without over-tightening to avoid damage of both the screw and material.
A4: It depends on the layers of materials the screw needs to join together and the thickness of the individual materials as to how long an M2 screw should be. A longer screw than necessary may cause material weakening by embedding too deep into them, while a shorter screw might not provide enough hold, secure, and free.
A5: The M2 screws are metric in nature, with a diameter of 2 mm, while the 2.5 screws are imperial, with a diameter of 2.5 mm.