(1529 products available)



















































































































































































































Electric sprocket motors are widely used and come in a variety of types. Each type has been designed to meet different application demands. Therefore, understanding the various types of these sprocket motors available is crucial when choosing one for a specific project. Below are some common types of electric sprocket motors.
Geared sprocket motors incorporate a gearbox between the electric motor and the sprocket. The gearboxes are meant to increase the torque and decrease the speed of the output sprocket. These types of sprocket motors are widely used in applications that require a high load drive at a slow speed. In addition to that, they are suitable for heavy-duty operations like conveyor systems and industrial machinery.
Brushless DC (BLDC) sprocket motors offer higher efficiency and longer operational life than brushed motors. They achieve this by utilizing an electronic controller to drive the motor windings. BLDC sprocket motors are popular in applications where precision control and minimal maintenance are required. Such applications include robotics, automotive components, and aerospace systems.
AC induction sprocket motors are powered by alternating current and are known for their durability and low maintenance costs. These motors work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. People commonly use them in fixed-speed applications where continuous operation is essential. Some of these applications include pumps, fans, and compressors. An AC induction motor sprocket is well adapted to such applications.
Stepper motors are used in applications requiring precise control of the speed, position, and torque. Their ability to make incremental steps provides smooth and accurate control over the output sprocket. Some of these applications include 3D printers, CNC machines, and robotics. These applications require high precision and control. Therefore, stepper sprocket motors are ideal for these applications.
Electric sprocket motors have practical uses across a multitude of industries due to their efficiency, power, and precision. Below are some of the industrial applications of electric sprocket motors.
Electric sprocket motors are widely used in the field of industrial automation. This is because these motors drive chains, belts, and other conveyance systems. These systems are widely used to move materials, components, and products through production lines. For industrial manufacturers, electric sprocket motors provide the necessary torque and control. This enables high-load handling and precise movement. Thus, increasing the operational effectiveness of conveyor systems, robotic arms, and automated assembly machinery.
In the field of robotics, electric sprocket motors are normally used to drive various mechanisms. Some of these mechanisms include wheels, arms, and joints. Their ability to deliver precise speed and torque control makes them particularly suitable for servicing applications. Some of these applications include collaborative robots (cobots), service robots, and robotic arms used in manufacturing, fulfillment centers, or other industrial settings. Moreover, these motors provide efficiency and accuracy. Hence, enabling robotic systems to perform their tasks effectively while still carrying a significant load.
The textile industry highly values electric sprocket motors for driving various machines. The machines commonly paired with these motors include looms, knitting machines, and fabric finishing equipment. These machines require great precision and control over speed and the direction of operation. Electric sprocket motors can efficiently handle the heavy-duty workload and intricate functionality of the textile machinery. This, therefore, enables better performance and more reliable production in the industry.
Aerospace systems require components that have high precision and reliability. For this reason, electric sprocket motors are commonly found in this industry. They are utilized in various systems such as actuation mechanisms, landing gear, and control surfaces. Electric sprocket motors also provide precise control over movement. Their lightweight constructions and high-efficiency ratings further enhance these motors’ suitability for applications in the aerospace sector to improve performance.
Electric sprocket motors are specifically designed using various features and specifications to provide efficiency and effectiveness in diverse application scenarios. These features influence the motor's performance, usability, and suitability for specific tasks. Below are the specifications and features of electric sprocket motors.
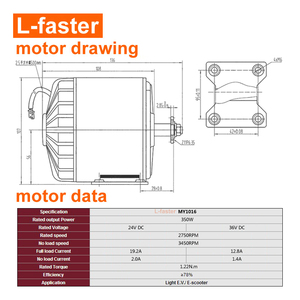
Torque is a key parameter of electric sprocket motors. It determines the motor's ability to drive loads. The torque output of these motors greatly varies based on the motor type and its application. However, it should be noted that high torque is particularly important in heavy-load installations. Such applications may include industrial conveyance systems, electric bicycles, and mechanical equipment. Therefore, knowing the required torque range helps in selecting an ideal motor for operational efficacy.
The power rating of electric motor-operated bicycles determines the bike's performance characteristics. As such, power ratings are measured in watts or kilowatts for sprocket motors. Generally, higher watt motors tend to produce more power and support heavier loads or faster operations. Sprocket motors rated at lower power are more suited to lighter duties. One also needs to balance the power rating with their application requirements to avoid under or overloading the system.
Electric sprocket motors are made of different materials. These materials largely influence the motors' weight, durability, and efficiency. For instance, motors made from aluminum or high-strength plastic alloys offer lightweight solutions for mobile or space-constrained applications. These applications include electric bicycles and miniature robots. Conversely, steel or brushed metal alloys have increased robustness. That makes them ideal for tough industrial settings, for instance, conveyor systems.
Electric sprocket motors come with different load-bearing capacities. These capacities depend on what the industry requires. For example, in manufacturing settings, motors packaged with high load-bearing capacities drive machinery and handle industrial tasks. However, in lighter applications like 3D printers, those with lower load-bearing capacities suffice. The load-bearing capacity of the motor in question should always match the application's demands to promote seamless operation and avoid early failure.
Choosing the right electric sportscars motor for one’s application requires several important considerations. This ensures the selection of a motor that meets performance and operational needs. Below are some of these key considerations.
Motor efficiency is another key factor to consider when selecting an operating motor for electric sportscars. This is because efficient motors convert a higher percentage of electrical energy into mechanical energy. They do this while ensuring less energy is wasted. Hence, this allows for lower operating costs and reduces heat generation and emissions. In addition, higher efficiency translates to better performance. To this end, considering the motor efficiency depending on the application is imperative when deriving an electric sportscar's performance and operational effectiveness.
Another key factor is the speed at which the motor operates. Different applications require different motor speeds. For instance, high-speed motors are ideal for applications like electric bicycles and scooters. Low-speed motors, on the other hand, are used in machinery to drive gears in industrial applications. Therefore, determining the proper speed range of the motor will ensure performance without excessive wear.
The first consideration is the industry in which the sportscars are operating. Factor in the environment where the motor will be working in. For example, if it is a dusty or wet environment, opt for a motor with an enclosed casing. Also, consider the duration of usage and load variations. If the motor is used for long hours, for instance, an AC motor would suffice due to its continuous running capacity. However, if it were used occasionally, a DC or stepper motor would work fine.
Materials normally used to make motors significantly impact their performance, durability, and weight. For instance, motors made of steel or other metal alloys are more robust. Thus making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications prone to wear and tear. Conversely, lightweight materials such as aluminum or high-strength plastic are ideal for applications requiring more mobility. These applications include electric bicycles or robotics. Considering the operating environment and load requirements will help select the most ideal material for the motor.
A1. These motors are electromechanical devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy using a sprocket connection. People widely use them in various applications that require movement or control of heavy loads. These applications include industrial automation, robotics, and transportation.
Electric sprocket motors combine an electric motor and a sprocket system to transfer power. The electric motor generates rotational force or torque. This torque is then transmitted to the sprocket using a chain or belt, which drives the connected load. The sprocket amplifies the motor's power, allowing it to handle heavier loads effectively.
These motors are not only efficient but also have high precision and control. Therefore, these factors make them ideal for various applications. Additionally, they have low operational costs and require little-to-no maintenance. They also produce less noise and are environmentally friendly compared to fuel-dependent drives.
The industries that commonly use electric sprocket motors include manufacturing, automotive, and packaging. Other sectors are aerospace, robotics, and material handling. These industries employ the motors in systems that require reliability, durability, and efficient load management.
Maintenance involves regular checks on the electrical connections, lubricating the sprocket chains or belts, and inspecting for signs of wear or damage. In addition, periodic cleaning removes dust and debris. They also ensure the components are properly aligned and that the motor is not overloaded.