(35642 products available)



































































































































































































 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship













A brake casting is a car part made by casting brake techniques, which helps to stop the car by creating friction in its wheels. There are usually three types of brake castings, which are discussed in detail below:
Discs
Brake discs are the most common type of brake casting in modern vehicles. They are typically made of iron, steel, or carbon compounds. The discs work by the brake pads creating friction and clamping the rotating discs attached to the vehicle's wheel hub. This friction generates a significant amount of heat that has to be dissipated for the braking system to work effectively. Ventilated discs with holes or grooves for cooling are common in high-performance and heavy-duty vehicles. Another variant are floating discs, which have two separate components that are allowed to move relative to each other for better heat distribution. The latter two types of discs are also the typical ones used in casting brake pressure washers.
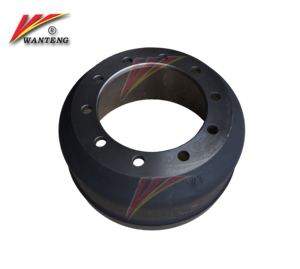
Drums
Brake drums are older types of brake castings and are not common in modern vehicles. These drums work by the wheel hub rotating the brake shoes inside the drum through the force exerted onto the wheels. The whole system works through the brake shoes expanding and creating friction against the inner walls of the drum. Magnesium, aluminium, and iron castings are some of the materials used in making brake drums.
Backup
Backup brakes are also known as oil brakes or wet brakes. They are usually used alongside casting brakes. The backup brakes work by using hydraulic pressure to squeeze the brake pads or drums, which creates friction to stop the vehicle or allow it to move at a desired pace. One advantage of backup brakes is that when there is excessive braking, like in the case where an entire mountain has to be descended, they do not overheat; they keep functioning normally. This is a significant advantage, considering that overheating brakes can lead to brake failure.
Material
Foundry brake materials are usually made of special high-heat brake pads. These pads are designed to withstand high temperatures generated during braking. This is to prevent brake fade from overheating, thereby ensuring stable braking performance. The durability of brake pads also affects the lifespan of brakes.
Machining
Foundry brake machining usually involves accurate machining processes such as turning, milling, drilling, etc. This ensures that the geometry and size of the brake parts are in line with the requirements, thus achieving proper fit and function. The precise machining also helps to reduce the vibration and noise generated by the brakes.
Surface treatment
Surface treatment of foundry brakes may include coating, plating, etc. These treatments improve the surface properties of the brakes, such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc. They prolong the service life of the brake parts and provide better braking performance.
Regular inspections
Regularly check the brakes to ensure that there is no damage, wear or other problems. If a problem is found, it should be repaired or replaced in time.
Clean the surface
Keep the surface of the brake parts clean. Use soft cloths and non-corrosive cleaners to wipe brake dust and dirt to avoid damage to the surface of the brakes.
Pay attention to lubrication
Some parts of the brake (such as the sliding surface) need to be lubricated to reduce friction and wear. Pay attention to add lubrication oil to these parts as required.
The foundry sector massively uses the brake casting. This is because it is both dependable and sturdy. The brake casting is in charge of slowing or halting surpassing vehicles. Additionally, trains' speed is reduced with brake castings.
Heavy machines also employ the brake casting. This includes equipment that are used in mining and construction. Such machines include excavators, wheel loaders, haul trucks, and bulldozers. This is because they require durable braking systems to safely manage the weight and operational requirements. In such cases, the braking system must be reliable and long-lasting.
Another popular use for brake castings is found in the automotive industry, where they are fitted into car wheels. Whether an electric vehicle or hybrid, all cars have brake castings.
Elevators frequently use brake castings to provide a smooth ride. And also ensure passengers' safety. The elevator brake casting is customized to allow it to be installed in the elevators. This is because elevators have to slow down or stop safely, especially when reaching the last floor.
Transformer trucks also utilize brake castings, especially in the mining sector. This is because, during the transformer change, casting has to effectively and quickly transform energy by changing the equipment's speed. Heavy-duty brake casting is ideal for handling the high energy transformations required during gear changes in mining applications.
In the railway industry, brake castings are found in trains. The trains require heavy-duty and strong and reliable brake systems to control the train's speed and stop safely. They have to be prepared to endure frequent usage, especially in long-distance traveling. More so in high-speed trains, accuracy and performance are of utmost importance. This ensures optimal safety and protection of the passengers.
When purchasing a new casting brake for business use, it is important to look beyond the initial cost to consider what will provide the least overall expense and most efficient equipment. It is well worth conducting a thorough analysis of needs and specifications before browsing models and suppliers.
Determine the size and capacity to create the volume of product needed, as well as the dimensions and weight of that product. Make a list of essential features that must be present, such as energy efficiency, speed, and ease of use. Standards for employees' health and safety and the environmental impact of manufacturing processes should also be considered. Also, research employees' skills and determine whether training will be required to run the new machine. Create a list of desirable features to be included in the casting brake, and be aware of the skills and age of the employees who will be using it.
When deciding on a casting brake, it is strongly suggested to begin with an analysis of the needs and specifications. Consider the following factors:
Q1: What is the difference between a casting brake and a casting swing?
A1: The primary difference between the casting brake and casting swing lies in their methods of controlling the movement of molten metal during the pouring process. While the casting swing is responsible for the actual pouring of molten metal into the mold, the casting brake regulates the speed at which it is swung or poured, thereby controlling the direction and rate of flow of the molten material into the mold cavity.
Q2: What materials are used for braking in cast iron?
A2: When it comes to casting materials, brakers are generally made up of high-quality non-ferrous materials. Almost all casting brakes are made up of bronze, brass, or other such materials.
Q3: How does the speed control affect the casting brake?
A3: The casting brake regulates the speed of molten metal pouring, ensuring accurate filling of molds and preventing defects in cast products.
Q4: Where is the casting brake located?
A4: Generally, the casting brakes are located in the foundries or metallurgical industries.