(1016 products available)




















































































































































































































Arden bits are cutting tools shaped like small wheels. They make a smooth place inside a hole. Different arden cutter tools carve, drill, or grind in unique ways. Users choose from various bits for their specific tasks. This section explores the major types of arden bits.
Cylinder-shaped arden tools are the most common type. The flat end lets them make even spaces inside holes. The wide cutting area gets rid of a lot of material fast. Users pick different widths based on how large the cavity should be. Fatter cylinders remove more material with each spin. These bits are great for tasks like finishing rough holes or shaping wide grooves in machines.
Tapered cylinder bits narrow towards the end. This shape allows them to make holes and grooves wider at the opening and fitting precisely deeper inside. The taper guides it to shape tight areas smoothly. Users pick cylinder bits based on the task. A tapered bit is ideal for creating flared holes or wide grooves that get snug down below.
Dome and ball bits are useful for rounding edges. The curved ends let them make smooth, rounded corners on parts. This is great for pieces that need the sharp edges removed. Dome bits create flat radii, while ball bits carve full hemispheres. Choose a radius based on the part's requirements. Larger domes and balls round the edges more than smaller ones.
Cylindrical arden diamond burrs are versatile. Their flat faces can grind down large areas or smooth out wide slots with ease and efficiency. Users pick these bits in various diameters depending on the task. Fatter cylindrical cutters cover more space quickly. Large cylinders are best for finishing big flat surfaces or hollowing wide grooves. Small cylinders provide precise control. They are perfect for tuning tiny channels or shaping delicate features.
Arden bits are durable cutters for machines. They maintain sharp edges and carves efficiently for a long time. Their materials make them resilient against wear, heat, and breakage. However, some factors can affect their lifespan. This section discusses the main elements that impact durability and how to care for arden bits.
The materials used to make arden bits contribute to their strength. Steel alloy bits work well but wear out faster. Cemented carbide bits last longer because they handle friction better. Users want durable bits for long projects. Tungsten carbide arden bits are ideal since they perform well under pressure for big jobs. Steel arbors have lower wear resistance. Therefore, these are best for short tasks.
The hardness of the material being cut affects the bit's life. Soft metals like copper do not wear down bits much, so they last longer. Cutting steel or hard alloys generates heat and friction that wear down bits quickly. Users choose bits based on their material. Hardened steel requires carbide cutters.
Heat can damage both the bit and the tool. Heat softens metals, which makes bits wear down faster. Lubricants cool the material and reduce heat. This slows down wear and helps the bit last longer. Users apply cooling fluid as needed. They pick lubricants based on the material.
Sharp bits carve better, which reduces pressure on the tool and part. This minimizes heat and wear. Users get better results with sharp tools. Buyers frequently check for dullness. A dull bit requires excessive passes, generating more heat. Users replace bits once dull.
Carbide bits attach to arbors for durability. Carbide alone is brittle, so it needs steel reinforcement. Users pick long arbors for wide bits. Short arbors work well for tightly detailed jobs.
Arden bits are valuable in many industries. Factories use them for tasks like shaping and finishing machine parts. They work well on metals, plastics, and more. Their precision makes them great for creating molds and dies. This section examines key uses and benefits of arden burrs in industry.
Manufacturers in aerospace and automotive rely on arden bits to shape important engine parts. The tools work on steel, aluminum, and titanium. Their precision creates parts that meet strict quality checks. Bits also carve complex molds that mass-produce these components. Consistent cutting makes work faster and cheaper.
Arden bits help gadget makers smooth plastics and metals. These bits make parts like phone casings and circuit board components. They ensure each detail matches designs. Polished bits enhance the product's look. Arden burrs also shorten assembly by uniformly carving complex shapes. This boosts production speed.
In construction, workers use arden bits to make molds for concrete tasks. The bits carve precise patterns into material. This assures each cast matches the builder's intent. Users make strong molds for beams and blocks, speeding home and structure building. Tough bits withstand large pours.
Arden bits play a vital role in medical device development. Doctors and factories depend on them to precisely shape. The bits work on steel and titanium for implants and tools. Each part meets strict health rules. Smooth bits enhance surgery tools' safety and efficiency.
Arden bits carve detailed patterns into costly molds. Factories use them to mass-produce identical parts. The bits assure precision, reducing errors. Users save money by avoiding material waste. Time-saving tools speed up production processes further.
Selecting the right arden bit can be challenging. Users consider many factors for the best outcome. This section explains the criteria for picking arden bits.
Different jobs need particular burrs. Smooth finishes prefer fluted bits, while fast cuts benefit from fishtail shapes. Cylindrical bits carve flat areas well. Users select profile cutters for custom tasks. Frontline companies consult experts when selecting or customizing bits for special tasks.
The material being cut determines the bit choice. Hardened steel needs durable tungsten carbide bits. Machine shops pick cobalt steel for general metal tasks. Gold and silver engraving use hardened steel bits. Rare makers choose carbide tip bits for custom tasks.
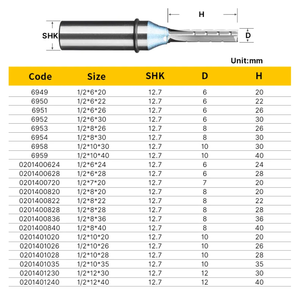
Bit size impacts user precision and speed. Wide bits remove much material quickly, while small ones allow detailed carving. Users think about their projects when selecting diameter and length. They choose large cutters for mass tasks and small for intricate work.
Buyers within industry groups consider these when picking bits. Consistency reduces assembly time in big tasks. Various profiles boost efficiency by satisfying diverse needs. They buy in bulk for cheaper rates.
Users weigh the number of bits needed against costs. Smaller sets suit light use, while industrial spaces require larger collections. Buyers hunt for deals but check quality first. Bulk buys are cheaper but only if bits last. Investing in solid carbide bits benefits long-term projects despite the higher initial expense.
A1: Most industries rely on arden bits. Car and plane factories use them to shape steel and aluminum. Tech companies smooth plastics for gadgets. Builders create strong molds with arden bits. The medical field depends on them for making safe tools. They work well on metals, plastics, and more.
A2: Both types make holes, but arden bits do more. Regular drill bits only cut simple holes. Arden bits carve complex shapes and detailed designs. They leave smoother finishes inside and outside parts. Factories prefer arden bits for their specialized tasks.
A3: Arden bits are often made from tungsten carbide. This strong material holds up for long tasks. Some bits are welded with cobalt for strength. Users select steel bits for more general jobs. These steel bits carve softer materials like wood and plastic.
A4: Yes, some arden bits, like pointed diamonds, are great for engraving. They leave clear marks on metals like gold and silver. Jewelers use these bits for precise designs. The bits carve intricate patterns that show details well.
A5: Each bit should go into its own space or holder. This protects the cutting tips from damage. Users mostly store them in hard cases or drawers. The case keeps dust and dirt out. The clean bits will cut smoothly when it is time to work again.